RDMA_Network_Guide
Identifying CX4/CX5 NICs
Run the following command:
lspci |grep Mellanox
Command output:
81:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27800 Family [ConnectX-5]
81:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT27800 Family [ConnectX-5]
Installing the MLNX Driver
Download the driver package that matches the OS from https://network.nvidia.com/products/infiniband-drivers/linux/mlnx_ofed/.
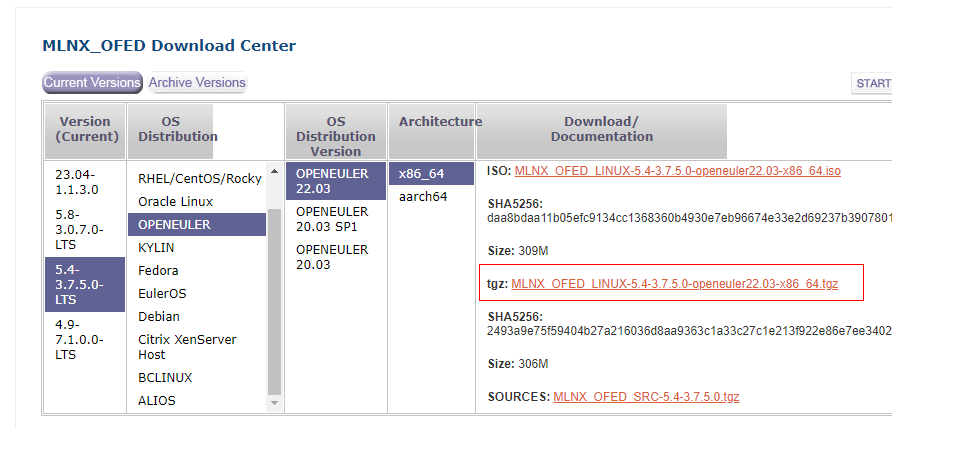
Create a directory and mount the OS image file to this directory. Change the OS image name to the actual one.
mkdir -p /mnt/iso mount openEuler-22.03-LTS-x86_64-dvd.iso /mnt/isoConfigure the OS image source, for example, the local image, to obtain dependencies required during the installation.
Open the image source file.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/openEuler.repoPress i to enter the insert mode and retain only the following content:
[OS] name=OS baseurl=file:///mnt/iso enabled=1 gpgcheck=0Press Esc, type :wq!, and press Enter to save the file and exit.
Cache the software package.
yum makecache
Upload the driver package to the server and decompress it. Change the driver package name to the actual one.
tar -zxvf MLNX_OFED_LINUX-5.4-3.7.5.0-openeuler22.03-x86_64.tgzGo to the driver package directory extracted after the decompression and run the following command to install the driver:
./mlnxofedinstall --without-depcheck --without-fw-update --forceIf the system displays a message indicating that the kernel does not support the driver version, run the following command:
./mlnxofedinstall --add-kernel-supportConfigure the system to automatically start the driver upon system restart.
chkconfig --add openibd /etc/init.d/openibd start chkconfig openibd onReboot the server after the installation is complete.
Verifying the Installation
Check the RoCE LAG function of the driver.
Check whether the RoCE LAG function is enabled.
find /sys/ -name roce_lag_enable | xargs cat- If the command output is 1, the function is enabled.
- If the command output is 0 or no command output is displayed, the function is disabled.
- The function is expected to be disabled. If the function is enabled, go to 1.b.
Disable the RoCE LAG function.
sed '/load_module mlx5_core/a\ files=`find /sys -name roce_lag_enable`;for file in $files;do echo 0 > $file;done' -i /etc/init.d/openibdReboot the node to apply the modification. Then, perform 1.a again to check whether the modification takes effect.
reboot
Query the driver version.
ofed_info -sIf the queried driver version is the same as the version installed in Installing the MLNX Driver, the driver version is correct.
Load the MST tool.
mst startIf the following information is displayed, the loading is successful.
Starting MST (Mellanox Software Tools) driver set Loading MST PCI module - Success Loading MST PCI configuration module - Success Create devices Unloading MST PCI module (unused) - SuccessQuery the device path and network port.
Query the device paths of RoCE and IB cards.
mst statusCommand output:
MST modules: ------------ MST PCI module is not loaded MST PCI configuration module loaded MST devices: ------------ /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access. domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:81:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1 Chip revision is: 00A device path /dev/mst/mst_typeN (N can be 0, 1, 2, ...) enumerated in the MST devices field indicates a CX card. For details about the mapping between mst_type and CX NIC models, see Table 1.
Table 1 Mapping between mst_type and CX NIC models
Query the network ports to be checked. Subsequent steps will check all the queried ports.
ll /dev/mst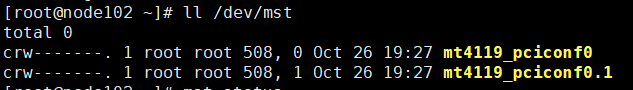
Ports mt4119_pciconf0 and mt4119_pciconf0.1 on the current node will be checked.
Check the firmware version.
Query the firmware version of the RoCE or IB card. In the command, /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 is the device path queried in the previous step. Replace it as required.
flint -d /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 qThe command output is as follows:
Image type: FS4 FW Version: 16.31.2006 FW Release Date: 31.8.2021 Product Version: 16.31.2006 Rom Info: type=UEFI version=14.24.15 cpu=AMD64 type=PXE version=3.6.404 cpu=AMD64 Description: UID GuidsNumber Base GUID: ec0d9a0300c152e4 8 Base MAC: ec0d9ac152e4 8 Image VSD: N/A Device VSD: N/A PSID: MT_0000000012 Security Attributes: N/A
Check the firmware network protocol.
Query the current network protocol. The ETH protocol is used as an example.
ibdev2netdev -v
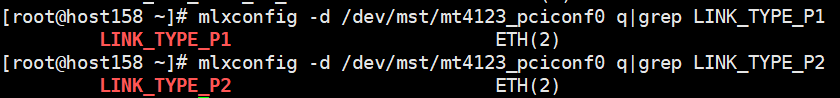
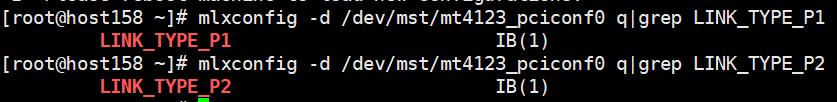
Query the values of LINK_TYPE_P1 and LINK_TYPE_P2. The following uses /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 as an example.
mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 q|grep LINK_TYPE_P1 mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 q|grep LINK_TYPE_P2- If the command output is empty, the network protocol cannot be changed in the current environment. In this case, change the environment.
- If the query result is displayed, the network protocol can be modified.
Change the values of LINK_TYPE_P1 and LINK_TYPE_P2. The following uses /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 as an example.
mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 s LINK_TYPE_P1=2 mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4123_pciconf0 s LINK_TYPE_P2=2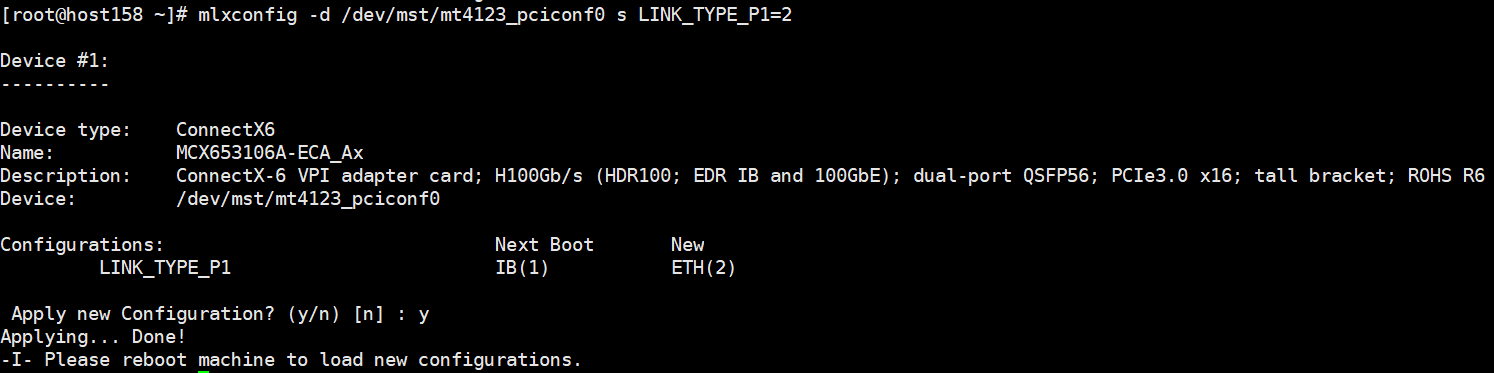
Run the reboot command to reboot the system and perform 6.b to verify that the modification is successful.
Run the following command on the server node:
ib_send_bw -d mlx5_1Run the following command on the client node (xx.xx.xx.xx indicates the IP address of the server node):
ib_send_bw -d mlx5_1 xx.xx.xx.xx(Optional) Set firmware options.
NOTE: You are recommended to perform this step to reduce the network delay.
Query the value of the CX card firmware option PCI_WR_ORDERING.
Take /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 as an example. Query the firmware settings of the two ports of the device. In the query result, the value of per_mkey is expected to be 1. If not, go to 8.b.
mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 q | grep PCI_WR_ORDERING mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0.1 q | grep PCI_WR_ORDERING
Set the firmware option PCI_WR_ORDERING for the two ports of a CX5 card, and run the reboot command to restart the system. After the environment is restored, perform 8 again to check whether the modification is successful.
mlxconfig -y -d /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 s PCI_WR_ORDERING=1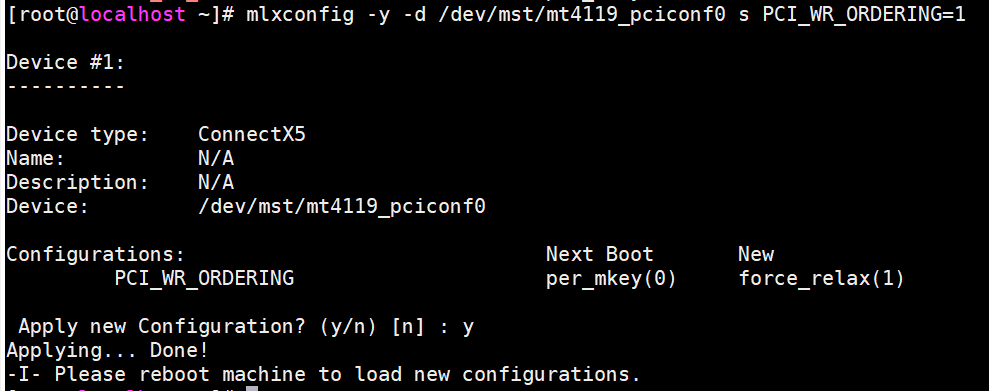
mlxconfig -y -d /dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0.1 s PCI_WR_ORDERING=1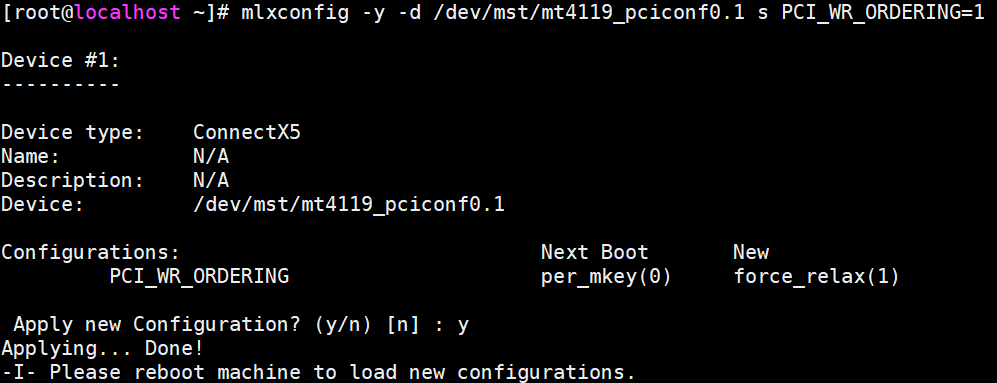
Configuring NIC IP Addresses
View the association between Ethernet devices and IB devices/ports.
ibdev2netdev -v- Name of the NIC associated with the NIC driver client mlx5_0 on the current node: enp24s0f0
- Name of the NIC associated with the NIC driver client mlx5_1 on the current node: enp24s0f1

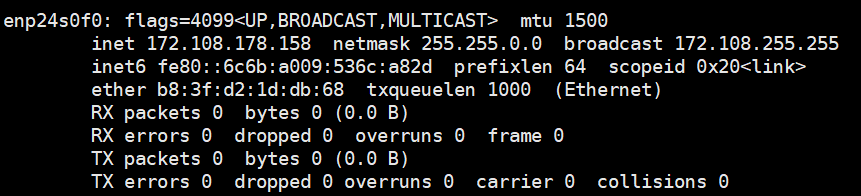
ifconfig -a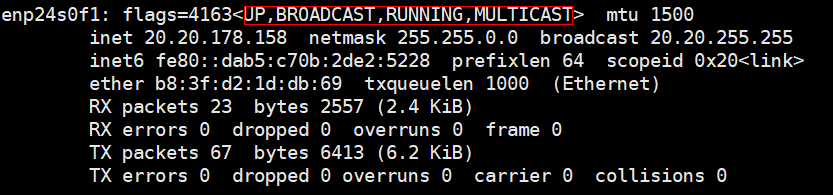
If the four states are normal, the NIC can be used properly.
- UP indicates that the NIC is enabled.
- RUNNING indicates that the network cable of the NIC is connected.
- MULTICAST indicates that multicasting is supported.
- MTU 1500 indicates the maximum transmission unit.
Configure the NIC IP address based on your environment. The following describes how to add the NIC IP address in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp24s0f0 configuration file. Run systemctl restart network.service to restart the application.
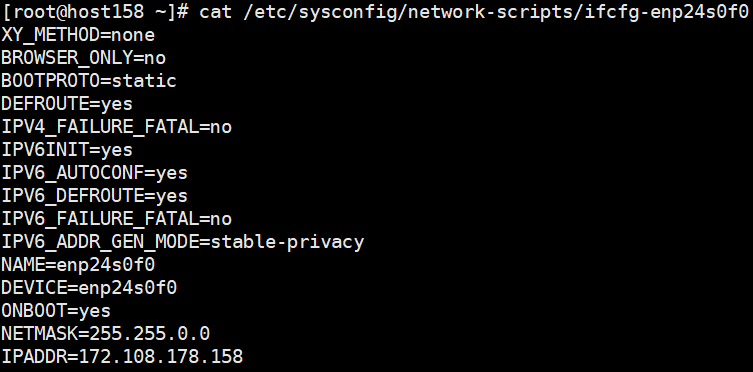
After the configuration is complete, check the NIC status by referring to 2.
Common IB Commands
Table 1 Common IB commands