openGauss
开源数据库
openGauss社区官网
开源社区
node exporter 自定义监控指标
2021-12-16node exporter 自定义监控指标
node_exporter 自定义监控指标
概述
node_exporter 除了可以收集系统指标外,还可以采集我们自定义的监控指标。采集自定义监控指标是通过 textfile 模块来完成的,textfile 模块默认会随着 node_exporter 启动而启动,如果想要采集自定义指标,还需要在启动 node_exporter 的时候,添加–collector.textfile.directory=""参数,这个参数是自定义的采集路径,所有自定义监控指标文件都放在这个目录下,且文件名都以.prom 结尾。
自定义指标
启动 node_exporter
--创建目录 # mkdir -p /opt/node_exporter/prom --以指定采集路径的方式启动 # nohup /opt/node_exporter/node_exporter --collector.textfile.directory="/opt/node_exporter/prom" > /opt/node_exporter/node_exporter.log 2>&1 &创建监控指标文件
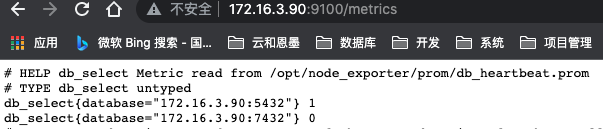
# cd /opt/node_exporter/prom # vi db_heartbeat.prom --HELP 和 TYPE 如果没有制定,node_exporter会自动添加 # HELP db_select Metric read from /opt/node_exporter/prom/db_heartbeat.prom # TYPE db_select untyped db_select{database="***.***.***.***:5432"} 1 db_select{database="***.***.***.***:7432"} 0在浏览器中可以看到,我们自定义的指标已经采集到
定时任务
自定义监控指标大多数需要与 crontab 结合,按着需求设置采集指标的时间。
flock 命令
为了防止某个任务的执行时间超过了 crontab 中为此任务设定的执行周期,使用 flock 命令将 crontab 串行化:
flock -xn /tmp/flock.lock -c ‘xxx.sh’ --如果/tmp/flock.lock 不存在,flock 会自动创建
Usage: flock [options] <file|directory> <command> [command args] flock [options] <file|directory> -c <command> flock [options] <file descriptor number> Options: -s --shared get a shared lock -x --exclusive get an exclusive lock (default) -u --unlock remove a lock -n --nonblock fail rather than wait -w --timeout <secs> wait for a limited amount of time -E --conflict-exit-code <number> exit code after conflict or timeout -o --close close file descriptor before running command -c --command <command> run a single command string through the shell -h, --help display this help and exit -V, --version output version information and exit For more details see flock(1).shell 脚本
这里以查询 MogDB 为例,通过 sql(select 1;)进行探活
vi /opt/scripts/db_heartbeat.sh #!/bin/bash source /home/omm/.bashrc nums=( ***.***.***.***:5432:opengauss_exporter:opengauss_exporter123 ***.***.***.***:7432:opengauss_exporter:opengauss_exporter123 ) for i in $(seq 0 $[${#nums[*]}-1]) do ip=`echo ${nums[$i]}|awk -F ':' '{print $1}'` port=`echo ${nums[$i]}|awk -F ':' '{print $2}'` username=`echo ${nums[$i]}|awk -F ':' '{print $3}'` password=`echo ${nums[$i]}|awk -F ':' '{print $4}'` result=`gsql "host=$ip port=$port user=$username password=$password dbname=postgres" -t -c "select 1"` if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "db_select{database=\"$ip:$port\"} 1" >> /opt/node_exporter/prom/db_heartbeat.prom else echo "db_select{database=\"$ip:$port\"} 0" >> /opt/node_exporter/prom/db_heartbeat.prom fi donecrontab
--执行脚本之前,先清理.prom文件,防止监控指标重复 * * * * * /usr/bin/flock -xn /tmp/flock.lock -c ">/opt/node_exporter/prom/db_heartbeat.prom && /usr/bin/bash /opt/scripts/db_heartbeat.sh >> /opt/scripts/db_heartbeat.log"