openGauss
开源数据库
openGauss社区官网
开源社区
title: '单表代价估计初探'
date: '2024-03-19'
category: 'blog'
tags: ['代价估计']
archives: '2024-03-19'
author: 'zhoujing'
summary: '通过分析一个单表查询的执行计划,了解sequence scan, index scan, sort等代价估计逻辑'
times: '19:30'
在分析一个分区表索引扫描,顺序扫描及排序的代码的过程中,学习并分析了一下相关代码估计代码。做个记录及分享。
1.创建分区表
create table top1 (
pk_report_asset character(32) NOT NULL,
c1 int, c2 int,c3 int, is_deleted smallint,
org_code int NOT NULL)
PARTITION BY LIST (org_code)
(
PARTITION p1 VALUES (1) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p2 VALUES (2) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p3 VALUES (3) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p4 VALUES (4) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p5 VALUES (5) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p6 VALUES (6) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p7 VALUES (7) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p8 VALUES (8) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p9 VALUES (9) TABLESPACE pg_default,
PARTITION p10 VALUES (10) TABLESPACE pg_default
);
2.增加约束
ALTER TABLE top1
ADD CONSTRAINT pk_top1 PRIMARY KEY (pk_report_asset, org_code);
3.产生数据库
insert into top1 values
(generate_series(1,1000000),
generate_series(1,100),generate_series(1,1000),generate_series(1,10000),
0,
generate_series(1,10)
);
4.收集统计信息
ANALYZE;
5.比较如下SQL语句的执行代价:
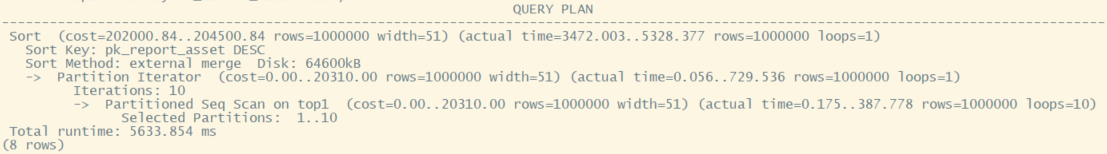
explain (analyze,timing) select * from top1 order by PK_REPORT_ASSET desc;
explain(analyze,timing)
select /*+ indexscan(top1 pk_top1) */ * from top1 order by PK_REPORT_ASSET desc
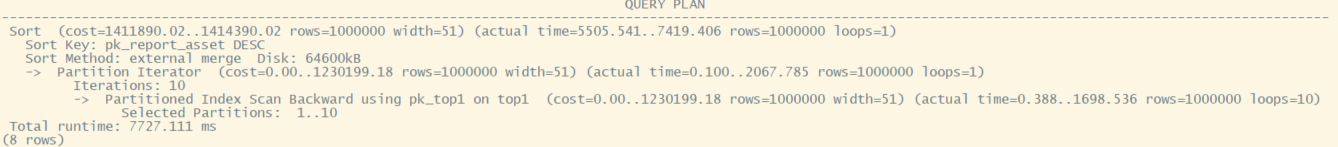
可以看到seqscan的估算代价20310比index scan代价1230199少很多,而实际运行时间729和2067,相差没这么大。而排序代价对于两种计划差别不大,详见下表。
| estimation cost | actual cost | |
|---|---|---|
| seq scan | 20310 | 729 |
| seq sort | 184190 | 4599 |
| seq total | 204500 | 5328 |
| index scan | 1230199 | 2067 |
| index sort | 184191 | 5352 |
| index total | 1414390 | 7419 |
所以下文主要分析一下,影响相关代码估计的因素,及其对应估算方法。
首先需要如下统计信息或配置信息进行收集:
cost estimation输入
| 统计信息 | 解释 | value | 获取方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nindex,page | index pages,analyze获得 | 12551 | select relpages,reltuples from pg_class where relname = 'pk_top1'; |
| Nindex,tuple | index tuples,analyze获得 | 1000000 | |
| Ntable,pages | table pages,analyze获得 | 10310 | select relpages,reltuples from pg_class where relname = 'top1'; |
| Ntable,tuple | table tuples,analyze获得 | 1000000 | |
| H index | index 高度 | 1 | 内存中结构获得 |
| var correlation | column correlation,列值排序与存储之间的相关性, analyze获得 | 0.0865771 | select correlation from pg_stats where tablename = 'top1' and attname = 'pk_report_asset'; |
| index correlation | index correlation,列值排序与存储之间的相关性,用于估计index访问造成的table io cost | 0.064932825 | index column number>1时候,0.75*column correlation,否则=column correlation |
| cpu_operator_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 0.0025 | |
| cpu_index_tuple_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 0.005 | |
| cpu_tuple_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 0.01 | |
| random_page_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 4 | |
| seq_page_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 1 | |
| qual_op_cost | postgresql.conf中配置 | 0 | 0.0025,此处没有qualification,故为0 |
| comparison_cost | 2*cpu_operator_cost | 0.005 | |
| dop | postgresql.conf中配置 | 1 | |
| sort_mem | postgresql.conf中配置 | 65536 | |
| Nsort,tuple | 计算获得 | 1000000 | |
| limit | sql语句中包含 | 720000 | |
| selectivity | 根据统计信息计算所得,此例中没有过滤条件故为1 | 1 |
sequence access
顺序扫描,也叫表扫描,顺序读取表中所有记录。计算公式如下表。start_up cost为0。
若打开并行,即dop>1, 则相关代价会除以并行数,此处为默认值1.
相关代码见costsize.cpp::cost_seqscan()
| seqscan cost | 计算公式 | 估计结果 |
|---|---|---|
| cpu_run_cost | (cpu_tuple_cost+qual_op_cost)*Ntable,tuple | 10000 |
| disk_run_cost | seq_page_cost*Ntable, page | 10310 |
| seqscan total cost | cpu_run_cost+disk_run_cost | 20310 |
index scan
index cost包括startup cost, index io+cpu cost,以及对应表的cpu+io cost几部分。
一般B树索引,是通过btcostestimate_internal这个函数计算indexTotalCost的,包含index cpu cost, index page cost及start up cost。该计划中indexTotalCost为55204.3
如果index scan可以访问到所有的列,也就不需要估计table的cpu 及io cost了,但本例中,index只包含两列,需要再访问表获取所有列的信息的。计算table io cost,需要根据index correlation来分析最好及最坏情况下table io的访问数目。再根据公式计算最终table io cost。该例子中min_io_cost为correlation为1时,table io为所有表页面顺序访问代价。max_io_cost为所有页面均为随机访问的代价,根据公式:max_io_cost+indexCorrelation* indexCorrelation*(min_io_cost-max_io_cost)
计算最终table io cost, 为1164994。已经远大于sequence scan代价。
| index scan cost | 计算公式 | 估计结果 |
|---|---|---|
| start-up cost | {ceil(log2(Nindex,tuple))+(Hindex+1)*50}*cpu_operator_cost | 0.3 |
| index cpu cost | selectivity * Nindex,tuple *(cpu_index_tuple_cost+qual_op_cost) | 5000 |
| table cpu cost | selectivity* Ntable,tuple *cpu_tuple_cost | 10000 |
| index io cost | ceil(Selectivity* Nindex,page) *random_page_cost | 50204 |
| table io cost | max_io_cost+indexCorrelation* indexCorrelation*(min_io_cost-max_io_cost) | 1164994.934 |
| Npages,(临时计算),考虑buffer cache的情况,在uncorrelated case下计算table pages | index_pages_fetched()apply the Mackert and Lohman formula 线性计算table io pages | 292471 |
| max_io_cost(临时计算),最差情况下所有table页都是随机访问 | max_io_cost=Npages*random_page_cost | 1169884 |
| min_io_cost(临时计算), 最好情况下所有table页按照顺序访问 | min_io_cost=1* random_page_cost+(ceil(selectivity* Npage)-1)*seq_page_cost | 10313 |
| indexTotalCost(临时计算) | indexTotalCost(临时计算)=index cpu cost+index io cost+ start-up cost | 55204.3 |
| total_cost | 1230199.234 |
sort cost
再看下sort cost。 本例子中,每个partition如果使用index访问,可以保证每个parition按照index key也就是PK_REPORT_ASSET 做了排序。最终结果集按照PK_REPORT_ASSET 排序后是否可以省略sort的代价呢?
这涉及到排序的实现方法。
在排序记录能全部放在sort memory中时,会使用快排序。在不能放在sort memory中时,会使用归并排序。本例中查询及排序的记录数较多,不能全部在sort memory中进行,故使用了归并排序。而归并排序的时间复杂度是O(Nlog2N)。即使所有partition已经按照PK_REPORT_ASSET排好序,最终结果需要将所有partition按照PK_REPORT_ASSET重新排序。时间复杂度仍为O(Nlog2N) 。
下面来看下具体sort cost的计算
| sort cost | 计算公式 | 估算代价 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| input_sort | sort之前的花费 | 20310 | |
| start-up cost | comparison_cost* Nsort*log2Nsort | 202000.8428 | |
| run cost | cpu_operator_cost*Nsort | 2500 | |
| io traffic | if(output_bytes>sort_mem_bytes) ,tape stype merge algorithm | 2* relsize * ceil(logM(p/(2*sort_mem))) | 82033 |
| total cost | 204500.8428 |
而无论sequence scan还是index scan的estimation cost及actual cost相差并不大。
小结
从上述分析我们看到,sort cost针对sequence scan与index scan并没有降低。而使用index scan会造成Npages较Ntable,pages增大很多,并且默认情况下index scan在correlation不是1的情况下产生更多的random io。而默认情况下 random_page_cost: seq_page_cost = 4:1 这个参数对SSD磁盘可能造成index代价估计过高。在调整random_page_cost=1后,估算代价与实际代价相近。但仍然会选择sequence scan。